Every business that competes in a local market and for localized results in Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs) will need to conduct local search audit regularly, apply diverse optimization strategies, and diligently work at improving the visibility and positive exposure of their business online.
Your potential customers are looking for the fastest path to the information they value. Google, the most powerful search engine on the planet, is working hard to serve the most relevant and personalized results to their users in the quickest way possible. Also, with the growth in the number of searches performed on mobile devices, proximity-based search results are more important than ever.

Google’s algorithm changes since 2014 (code names Panda, Penguin, Hummingbird, and Pigeon) have had a disruptive impact on search results, including local search. The Pigeon algorithm shook up the local search engine optimization world by giving greater weight to local businesses that have neighborhood-focused keywords and by connecting Google maps search and web search more cohesively.
Starting in 2017, it is becoming much harder to compete for free traffic in Google’s local search results, known as the 3-pack. Not only are you fighting against competitors who are trying to get the same ranking and against 4+ ads before customers have the possibility of seeing your business, but you are also additionally fighting against paid listings prioritized in local results.
What does all this mean for local businesses? Focusing on local search should be a strong priority for you, even if you don’t have a pay-to-play budget for ads. Getting listed in the local finder can result in easy wins. If you want to beat your competition and show up on top of the local search results, you will need to know where you stand and what you need to fix. Knowing this, you can then develop a plan to win, based on the competitive landscape and the understanding that users desire to get to value with minimal clicks. This is where effective local search optimization becomes crucial. However, as with any marketing program, be careful not to have a tunnel vision on just free local clicks. Instead, expand your strategy to be sure you focus your efforts on where your customers are looking and how you can get in front of them.
In this article, I will offer a detailed checklist to show you what areas you should focus on, what needs to be optimized, and what you need to do to fix any problems you encounter to best position yourself for local search traffic and business. I will also discuss strategic insights for a customer-focused and data-driven strategy to evolve your program.
1. Start with a comprehensive audit
 Through experience with many clients throughout the world, we at WSI have found that we can provide the best results when we start a project off with a complete and holistic understanding of the client situation. When we have a complete snapshot of your current SEO efforts, along with an understanding of your competition, we can create a plan that is going to be much more effective and sustainable. We recommend that you regularly conduct an audit and maintain an organized worksheet to record and track your progress.
Through experience with many clients throughout the world, we at WSI have found that we can provide the best results when we start a project off with a complete and holistic understanding of the client situation. When we have a complete snapshot of your current SEO efforts, along with an understanding of your competition, we can create a plan that is going to be much more effective and sustainable. We recommend that you regularly conduct an audit and maintain an organized worksheet to record and track your progress.
For the audit, you will need to evaluate and consider the work performed in prior SEO efforts to uncover potential damage that has been done. Always start your local SEO plan with a comprehensive audit.
The following areas can be used as the checklist categories and items to include in your audit as well as for quality assurance of your local search program.
2. Website & Landing Page Optimization
Having a properly optimized site is more important than ever for organic and local search. Organic signals are now more tied into the local algorithm and having a properly optimized website will help you outrank your competition. Besides, if your website isn’t loading fast, you’re losing conversions.
The landing page optimization activities focus on the page to which the Google My Business (GBM) links. Typically, a single location business might have all of the pertinent information on their homepage. If you have multiple locations, it makes sense to create a page for each location and ensure all the pertinent pieces of information are covered.
The followings are activities relevant to the local landing page optimization:
- Correct “crawl-able” Name, Address, Phone Number (NAP) information on the local landing page(s) – The landing page footer should have NAP information in crawl-able HTML text format, and it needs to match the NAP on your GMB profile. It is important that your NAP is not an image as search engines would not be able to see it.
- NAP in hCard / org business markup – You want to use Schema.org markup on your NAP to give the search engines what they need to display your company information correctly. You can learn about hCard formatting for local search here.
- Business hours – If your business hours are located within an image keep in mind that Google bot will be unable to read it.
- Site structure – structure that meets your long-term optimization goals, which includes the city and state if possible and provides a helpful user experience.
- Landing page content – Be sure you have at least 500 words of unique and helpful content focused on creating a great user experience. More is better and it should include the city and state.
- Indexed landing page – Verify that your landing page is indexed. You can do this with a quick Google search by looking for the landing page URL in private browsing mode (e.g., Incognito search mode in Chrome). If your site shows up in the results, then the page is indexed.
- Landing page meta title tag – Ensure your landing page meta title contains the city and state and is helpful to users.
- Meta Description – The meta description is the text that shows in the search results underneath the title. The meta description should include the business name, city, state, and local phone number.
- Heading tags (H1) – Ensure that you only have one H1 tag. It should have the city and state in the tag.
- Driving directions & embedded map on landing page – Your landing page should have driving directions, including an embedded map. You can get, and embed the Google map code for your listing from maps.google.com.
- Customer reviews on page in Schema / hReview – It is good to have at least one written customer testimonials that display in Schema or hReview. The more, the better.
- Alt text on landing page – If you have images on your landing page you should have image ALT tags. Your ALT text should include the city and state if appropriate.
- Load time of landing page – Pages should load in 2-3 seconds at 1.5Mbps load rate. There are many tools to measure site speed. GTMterix is a good one.
- Domain authority (DA) of website – You want the highest domain authority over your competitors. You can use MozBar to check this.
- Content keyword stuffing – Use keywords in the copy naturally and to be helpful, not to manipulate a site’s ranking in Google search results.
- Mobile friendly website – be sure your design elements are properly rendered on mobile devices.
- WHOIS information – Check the WHOIS Information and ensure the NAP matches the main location. You can do a WHOIS check here.
- Google Analytics – Make sure Google Analytics is installed.
- Google Search Console – Ensure Google Search Console (GSC) – previously known as Google Webmaster Tools – is configured properly. Also, check your Bing webmaster tool.
3. Basic Location Information
Correct all discrepancies and inconsistencies in business Name, Address, Phone number (NAP) and other related information. Also, ask questions about previous business names or previous experience with SEO or SEO penalties.
- Be sure that your NAP is consistent across the Internet, especially the top-ranked directories.
- Check that all the data points of your business on every local citation (i.e., directory listing) align perfectly.
4. Analyze and Maintain “Google My Business” Page
Find the proper Google My Business (GMB) URL and record it in your Local SEO Audit Spreadsheet. Follow Google’s guidelines to assure your business NAP, category, and subcategories, and other items are represented properly on your MB listing. The followings are GMB audit activities:
- Locate and claim the proper GMB page.
- Find and destroy duplicate listings.
- Ensure local listing is not penalized.
- Make sure your GMB is associated with a valid business email address (i.e. not a generic Gmail address)
- Listing is verified.
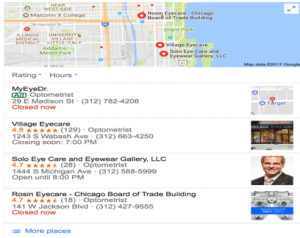
- Correct business name.
- Correct address.
- The correct phone number that is consistent with your website and other listings (i.e. not an 800 number).
- Proper URL to the right page on the website. Depending on your site structure and number of locations you have, it may make sense to link to either the home page of your website or a landing page that is designated to that location.
- Proper category and sub-categories selections.
- High-quality profile, cover page, interior, and exterior photos/images.
- Accurate business hours.
- Profile 100% complete.
5. Reviews & Reputation Management
Local reviews have a direct impact on local search rankings; they can make or break a local business regardless of how well their keywords can rank. So, you’ll want to spend some time acquiring them in a manner consistent with the directory or service. For any directory, we strongly discourage paying for reviews.
It is disheartening how many businesses are not paying attention to controlling their online reputation. With reviews, there are several attributes to address, including:
- Positive Sentiment – A positive sentiment helps increase the search engine and consumer confidence in your business
- Uniqueness – avoid replicating the same exact review across different web pages — they may be ignored.
- From Power User – some services like Yelp have power or elite users where reviews from those users carry more weight.
Google My Business reviews – Do you have at least 10 reviews with a 4 star or higher aggregate. If not, work on it. In some industries, 10 reviews are just a starting point. Reviews must be natural, legitimate, and be left for a business according to the guidelines. Unlike Yelp, Google guidelines allow you to remind customers to provide a review.
Top third-party review sites – Record the major third-party review sites for your niche. Ensure they have at least 5-10 reviews with at least a 4-star rating. Depending on your niche, look at Google Analytics and check out the referral traffic. Sort this by the top referrals and see which sites are sending the most traffic to your site. If they allow reviews it’s a good idea to raise your rating by adhering to the third-party reviews site’s guidelines and obtaining them when possible. Also, read bad reviews and be sure to address them.
- A proper response to negative reviews – start with a sincere apology and take action to address the issue. You may also take the issue offline if the directory allows it (Yelp does). If the review is in violation of the directory policy, request that it is removed. Otherwise, the best way to overcome negative reviews is to have a lot more positive reviews.
For more information on reviews, you may want to check this article on getting 5-star reviews on Quick Sprout
6. Citation Analysis and Continuous Improvement
Get relevant & high-authority citations. The quality of citations is more important than the quantity. Citations are simply the listings of your business name, address, and phone number (NAP) on the web. Some citations are structured, like your Yelp listing, and these are sanctioned business directories. There are also unstructured citations. Unstructured citations are mentions of your NAP on websites that are not necessarily a business directory. For example, if your business is mentioned in the local newspaper they might also include name, address, and phone number in their online article.
Citations may have been created by you, or they may have been created by aggregators that sell the information. Regardless of how they were created, you want to be sure the information is accurate and represents your business in the best light. This is a part of managing your reputation online; you need to control it. Listings are important for local search, and more importantly, they are critical for your online visibility and reputation. If your business has duplicate listings it will not only hurt your local SEO rankings, but your customers might not find the right listing and therefore leave, or see incorrect information or outdated reviews.
The goal of your citation building it to ensure that your business is listed, that there are no duplicates, and that the information is 100% correct on the top 50 citation sources and all of the data aggregators. Whitespark’s list of the top 50 citations or Hubspot’s blog on the subject will help you with this analysis. Keep in mind that you also want to verify your presence with an iOS device and ensure your business is listed in Apple Maps.
These are the items to include in your citations optimization activities:
- Check data aggregators and the top 50 citations – These are companies that supply business databases for local search directories. They are the data holders that submit your business information to other directories. The main data aggregators in the United States are Infogroup, Localeze, Acxiom, and Factual. Make sure your business is listed correctly without duplicates by these aggregators and is in the top 50 listings. The best way to start this is through MozLocal. It is worth the cost because if you wanted to check the aggregators yourself, it would cost you a lot more than the cost of a MozLocal yearly subscription.
- Identify new high-quality citation sources – If your top 50 citations are in good shape, there may still be a few more you want depending on your industry. You might want to get quality unstructured citations or mentions in local and major newspapers and publications when possible. Additionally, learn which niche sites are available for your type of business. Brightlocalhas a great resource to find niche specific citations.
- Establish an ongoing local link building strategy. Check out this guide by Mathew Barby in SearchEngine for a creative list of local link building strategies
- Verify your business is on Apple Maps – Visit Apple Maps Connect, login, and make sure your business NAP is correct.
7. Organic Link Building & Penalty Analysis and Correction
If you are taking over an existing website, it is important to do a link and penalty audit and to assure that you are growing natural, high-quality links. You need to keep the site out of a penalty short term and long term. You need to identify any potential problems and prepare yourself or your client to make effective business decisions. Google penalties can be brutal, and recovery is not a walk in the park.
As stated earlier, since the Pigeon Update Google has put more weight on high-quality links and overall authority into the local algorithm. So, don’t get or buy links for links’ sake. Links are earned through high-quality content you produce or news mentions you get. Quality is much more important than quantity.
Link building audits are tedious and experience is key. Although there are tools to make this job easier, tools are also imperfect and you need an experienced person is needed to do an effective audit and maintain high-quality links. The following are key activities and outcomes of a link and penalty audit:
- Verify that there is not a manual webspam action – Be sure that your site is verified with Google Search Console (GSC), then in GSC, simply click on the manual actions tab to make sure there are no penalties. If there are, this will become your top priority to fix.
- Check for algorithmic penalties – Start with Google Analytics to spot trends. You can use a tool that will align your traffic numbers with the dates of known algorithmic updates. The Panguin tool makes this easy. Although this can be tricky, your goal is to determine if there are any algorithmic penalties and what you can do to fix them. This Moz guide on Google Algorithm changes can be helpful.
- Number and quality of links relative to your competitors – Record the number of links to your landing page and root domain and compare it to your competitors. This will help you identify potential issues with spammy links and take immediate action to fix them. You can do this using the MozBar.
- Anchor text of links – Anchor text is the text that appears highlighted in a hypertext link and that can be clicked to open the target web page. Your anchor text distribution is very important to organic SEO. Your link profile should appear natural and the quantity of them will depend on your industry. Brand anchor text should always occur more often than commercial keywords. Here is a guide by Powered By Search to help you conduct this analysis.
- Link velocity – Avoid building too many links fast. If you write something great and it goes viral, that’s wonderful. Make sure that the speed at which you build links is natural. Review any spikes for problems.
- Disavow File – Be sure the disavow file in GSC exists and is updated monthly to include any bad links whether they were intentional or from negative SEO. This will be your saving grace if an algorithmic penalty exists and there is a Penguin update which takes any disavow you may have into consideration.
8. Social Analysis
Social media and local SEO have some crossovers related to the NAP, check-ins, and brand consistency. You can also get benefits locally from geo-tagged content and video sharing of geo-tagged content on sites like YouTube. Include your NAP in the description of your videos and try to increase conversions by creating high-quality videos. Be sure not to have duplicate social profiles on any social platform.
Review your profiles – Facebook, GooglePlus, Foursquare, Twitter, Linkedin Business page, Youtube, Instagram, etc.–and verify they have consistent branding, NAP consistency, high-quality photos, business description, positive reviews, description, effective geo-targeting, and other elements in accordance with the guidelines of the platform.
It is important that you are posting regularly to these platforms for them to be useful
9. Competition Analysis
There are several insights that you can take from analyzing your competitors’ online presence. This will help to both inform your strategy and develop an action plan that is in line with Google’s guidelines. One thing you should do for sure is to review their links and citations and see if you missed any of the high-quality easy wins they have. Do not try to duplicate all their profile, but focus on high-quality relevant links for your industry and location.
Here are the activities to consider in a competitor analysis:
- Identify them – Find 3-7 competitors for your niche and record them in the spreadsheet with their NAP and GMB Page information.
- Conduct and record the competitor analysis related to the following factors:
- Figure out the domain authority of their root domain using the Moz Toolbar
- Figure out the page authority of the Google My Business landing page using the Moz Toolbar.
- Number of links from the root domain.
- The number of links each has from unique domains.
- Number of citations and the ones that are detected.
There are several tools that help make this audit easier, including Moz Local, Brightlocal, Whitespark.
With this analysis, you’ll have a snapshot of your strengths and weaknesses relative to your competitors and develop an idea of where you will want to be. You can then develop an informed strategy to get more authority from stronger sites and develop your brand online.
10. Evolving and Expanding your Strategy
Although local search prowess is very important for local business. The digital search dynamics are constantly changing. It is important to take a step back on a regular basis and consider your strategy by asking questions to be sure your program is current and focused on your customers. Here are a few questions you want to be asking in light of the trends in 2017:
- What websites, other than your business, have the most visibility for the topics and keywords relevant to your business?
- Are your customers using voice search?
- Are you optimizing for “near me” searches? These have been on the rise.
- Should you be doing more ads, especially in the local pack?
- Should you be looking at if and how snippets can help your business?
Conclusion
Having top rankings in the local search research is important for businesses competing for local business. Organic search algorithms and local search algorithms are constantly changing and becoming more intertwined. And, organic and local search are having to increasingly fight with increased numbers of paid ads for showing up on top of the search result page.
So, a local business focused on growth needs to master the 10 basic areas discussed in this article, which needs a systematic and consistent approach. You also need to remain focused on the broader goal of increasing traffic and customers, as opposed a one-dimensional focus on local search alone. In this regard, you need a diversified, data-driven, and open-minded strategies that are going to get your business more customers.
References Neil Patel: How to Attract Local Customers: A Complete Guide to Local SEOMoz - Casey Meraz: How to Perform the Ultimate Local SEO Audit Seach Engine Land: Matthew Barby: Local SEO: How To Rank Your Local BusinessJon Cooper: Link Building Tactics Bakclinko: Link Building: The Definitive Guide Juris Digital: 21 Link Building Tips Nifty Marketing: The Ultimate List of Local Link Building Ideas

Stay Connected